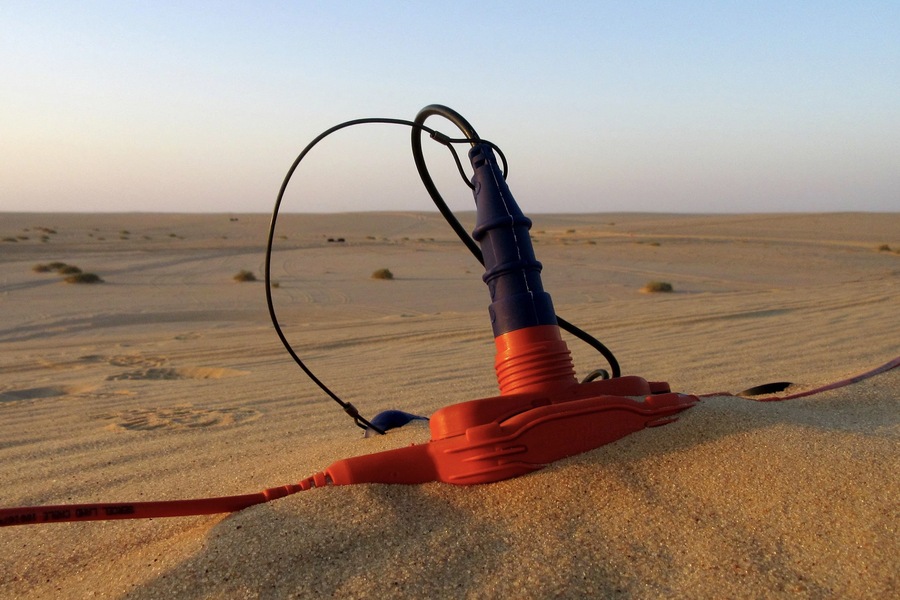
Seismic exploration is a specialized field of exploration geophysics, which plays a crucial role in studying the Earth’s subsurface structure. This method is based on the recording of artificially excited elastic waves (seismic waves), which are used to extract valuable geological and geophysical information. The use of seismic waves has been one of the leading methods for studying rock formations, particularly in regions like Al Ain and other parts of the Middle East. Due to its effectiveness, seismic testing Al Ain is widely used for identifying natural resources, assessing hydrogeological conditions, and solving engineering geology problems.
History and Evolution of Seismic Exploration
Seismic exploration emerged as a method in the early 1920s, primarily for the oil and gas industry. Over the decades, advancements in technology and methodology have made seismic testing an essential tool in geophysics. Its ability to provide detailed imaging of underground structures revolutionized the way geologists study the Earth’s crust and locate valuable mineral deposits.
The underlying principle of seismic exploration involves generating elastic waves, usually through an artificial source, and recording the way these waves reflect or refract as they travel through various geological layers. By analyzing how these waves behave, geophysicists can create a graphical representation of the Earth’s underground structures.
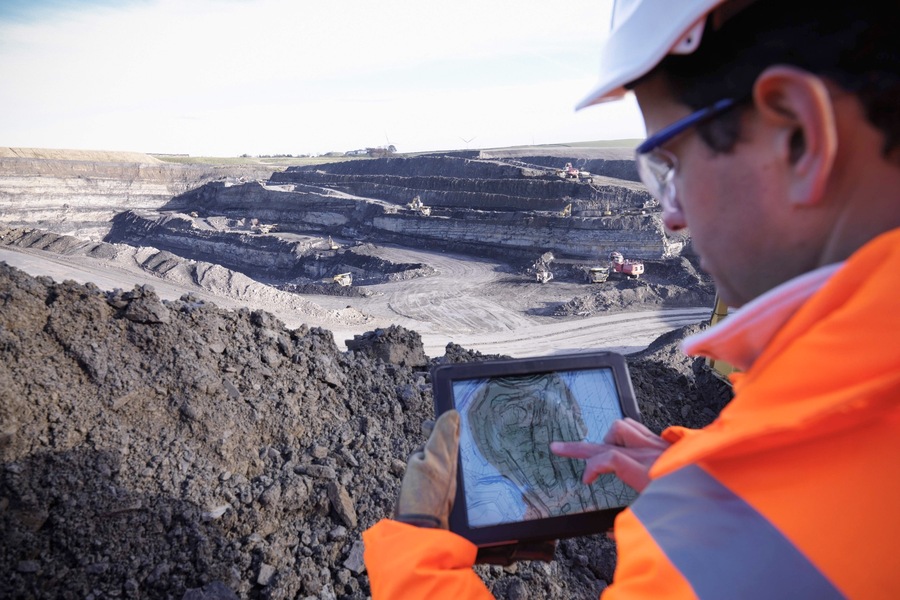

Applications of Seismic Exploration
Seismic exploration has a wide range of applications across several geophysical and geological fields. Some of the key areas of application include:
1. Oil and Gas Exploration: The most significant application of seismic exploration is in the search for oil and natural gas deposits. It helps exploration companies create detailed maps of the Earth’s subsurface, allowing them to pinpoint potential hydrocarbon reservoirs accurately. This approach is not only cost-effective but also reduces the risks associated with exploratory drilling.
2. Mineral Deposits and Hydrogeology: Beyond oil and gas, seismic methods are used to locate other mineral deposits and study groundwater resources. Seismic data provides insights into the composition and structure of the rock formations, which are crucial for water management and mining activities.
3. Marine Seismic Exploration: Seismic exploration plays a critical role in marine environments, especially in offshore oil and gas exploration. In marine settings, it is the dominant method used due to the vast, inaccessible nature of underwater formations. Marine seismic exploration surpasses land-based exploration in volume by more than four times and continues to grow.
4. Engineering Geology: Seismic methods are widely employed in engineering projects for understanding subsurface conditions before the construction of large infrastructures like dams, bridges, and tunnels.
5. Seismic Microzoning: This technique is essential for assessing local seismic hazards and determining the vulnerability of regions to earthquakes. Seismic microzoning provides information that is crucial for designing earthquake-resistant structures and urban planning.
Seismic Exploration in Al Ain and the Middle East
In the Middle East, particularly in Al Ain, seismic exploration is one of the leading methods for studying the subsurface. The region’s rich hydrocarbon reserves make it a prime location for seismic surveys. The Middle East, as a whole, heavily relies on seismic testing to evaluate potential oil and gas reserves, especially in offshore regions.
The geological conditions in Al Ain, characterized by complex formations and a thick sedimentary basin, make seismic exploration an indispensable tool for understanding the area’s underground structure. Seismic surveys in this region involve covering vast land areas, sometimes extending over thousands of square kilometers, and deploying dense networks of seismic sensors.
Seismic Exploration Technology
Seismic exploration utilizes elastic waves to probe the subsurface. This is achieved by creating waves through an artificial source (such as an explosive or a vibrational device) and recording how these waves travel through the Earth’s layers using seismic receivers. The following are key elements of seismic technology:
– Seismic Receivers: These devices convert mechanical vibrations caused by the seismic waves into electrical signals. Seismic sensors are deployed in vast networks to capture detailed information across large geographical areas.
– Sources of Seismic Waves: There are several types of sources used to create seismic waves, classified by wave type, dimension, and source type.
– By Wave Type:
– Reflected Wave Method (RWM): This method records waves that bounce back after hitting geological interfaces.
– Refracted Wave Method (RWM): This method records waves that bend as they pass through different layers of rock.
– Vertical Seismic Profiling (VSP): This method involves placing receivers inside a borehole to capture detailed information about the surrounding subsurface.
– By Dimension:
– 1D Surveys: Where the source and receiver are located together.
– 2D Surveys: The source and receiver are aligned along a straight line.
– 3D Surveys: A grid of receivers is distributed across an area to capture data from multiple directions.
– By Source Type:
– Explosive Sources: Using controlled detonations to create seismic waves.
– Vibrational Sources: Often used in urban environments where explosives are not feasible.
– Non-Explosive Pulsed Sources: An alternative for creating seismic energy without using explosives.
– By Frequency Range:
– Low-Frequency (1-10 Hz): Ideal for exploring deep geological layers.
– Medium-Frequency (10-100 Hz): Useful for mid-depth surveys.
– High-Frequency (>100 Hz): Employed for shallow subsurface studies and higher resolution imaging.
The Importance of Marine Seismic Exploration
The exploration of hydrocarbon deposits at sea is a crucial application of seismic exploration. In offshore areas, seismic surveys are practically the only effective method for locating oil and gas reservoirs. These surveys are carried out by using arrays of seismic receivers and sources deployed on ships. As seismic waves propagate through the seabed, the reflected waves are recorded and analyzed to provide a detailed image of the subsurface.
Due to its high effectiveness and reliability, marine seismic exploration is continuously expanding. The sheer volume of data obtained from these surveys makes it a leading method for offshore resource identification.
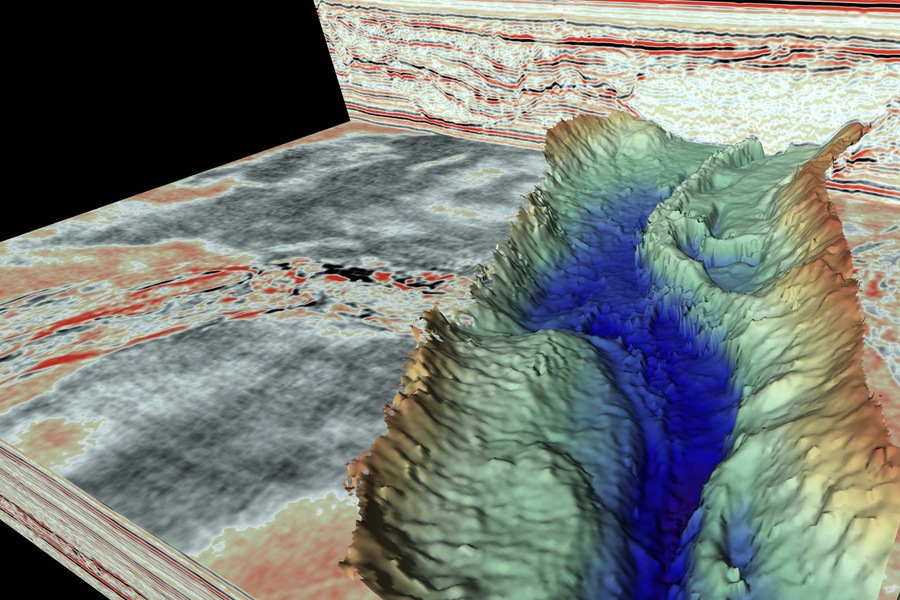
Advantages of Seismic Exploration
Seismic exploration remains the most reliable geophysical method due to its:
– High Resolution: Seismic methods provide detailed imaging of the Earth’s subsurface, which helps in accurately identifying hydrocarbon reservoirs.
– Technological Effectiveness: With advancements in technology, seismic methods have become more efficient in both data collection and analysis.
– Enormous Data Volume: The use of networks of thousands of seismic sensors allows for the collection of large datasets, which can be processed to reveal detailed underground structures.
Conclusion
Seismic exploration has been a cornerstone of geophysical studies for over a century. In regions like Al Ain and other parts of the Middle East, it continues to be a leading method for studying the subsurface and identifying oil and gas deposits. Its ability to provide detailed and reliable information about geological formations makes it indispensable not only for resource exploration but also for a range of engineering and environmental studies. As technology advances, seismic exploration will continue to evolve, offering even more precise and efficient ways to understand the Earth’s hidden structures.

I act as a financial expert on the Today Show and Good Morning, America. I like to give reasonable advice on budgeting to people with any income level.